Diabetes is defined as a chronic disease when there are high levels of sugar in the blood. The three major types of Diabetes are Type 1, Type 2 and Gestational Diabetes. Type 2 Diabetes makes up most of the cases and it is diagnosed with a fasting blood sugar level higher than 126 mg/dl measured twice. Levels between 100 and 126 mg/dl are referred to as impaired fasting glucose or pre-diabetes. Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) is used to measure the average blood glucose concentration over prolonged periods of time. This test gives an average of what your blood sugar levels have been over the past weeks to months. A normal HbA1c is less than 5.7%, Pre-Diabetes is 5.7% – 6.4% and 6.5% or higher is considered Diabetes.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes, also called Non-Insulin Dependant Diabetes, often occurs in adulthood, but children, teens and young adults are now being diagnosed due to climbing obesity rates.
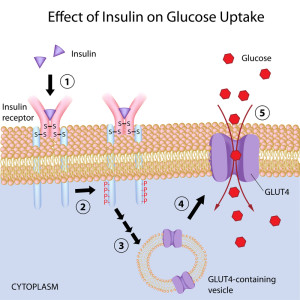
The root cause of Diabetes is a diet high in carbohydrates combined with the nutrient deficiencies that usually occur with this type of diet. Your body breaks down carbohydrates into sugar, and the more you eat, the higher you blood sugar goes. In response to climbing blood sugar, your body produces insulin from the pancreas, which then puts the blood sugar into your cells. We utilize sugar for energy and need it in our cells, but after many years of consuming a high carbohydrate diet, your cells become overwhelmed and blood sugar cannot get in anymore. This is called insulin resistance.
Diabetes affects more than 25 million Americans and over 80 million Americans have pre-diabetes (early type 2 diabetes).
One out of four people in the United States over the age of 65 years have Diabetes.
Type 2 Diabetes develops slowly and some people will have no symptoms, but it can cause blurry vision, excess thirst and hunger, dry mouth, nausea, fatigue, frequent urination, and slow healing of wounds.
Complications of Type 2 Diabetes
Since your blood continues to get thicker as the sugar in your blood increases, Diabetes can lead to serious problem such as:
- Vision impairment and light sensitivity
- Impaired wound healing. Feet and skin can develop sores and infection
- High blood pressure and cholesterol become more difficult to control, which can lead to heart attack, stroke and other problems
- Nerves damage, causing pain, tingling, and loss of feeling
- Kidney damage
Causes of Diabetes
- Overweight, Obesity
- Increased body fat makes it more difficult for your body to use insulin the correct way and because of this most people are overweight when diagnosed with Type 2 Diabetes. Four out of five people with Type 2 Diabetes are overweight or obese. Excess fat, especially around the abdomen, changes the way your body responds to insulin. You cells can no longer use insulin as efficiently to take sugar out of the blood.
- Processed Foods and Beverages
- Eating lots of calorie-dense, refined and processed food and beverages, such as sodas and fried food, and too little raw fruits, vegetables and whole grains, dramatically increases your risk for Type 2 Diabetes.
- Sedentary Lifestyle
- Watching too much TV has also proven to raise your risk. Based on an analysis of health and nutrition data, people between the ages of 20 and 54 years of age who watched TV more than two hours a day were more likely than their peers to be obese and have diabetes.
- Physical inactivity is another risk factor for Type 2 Diabetes. Exercise and strength training will increase lean muscle mass and help protect the body against insulin resistance.
Research
- According to an article titled, “Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus by Lifestyle, Diet and Medicinal Plants (2011)”, among the non-communicable diseases diabetes is increasing at an alarming rate. If not controlled, complications like coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular disease, peripheral vascular disease, retinopathy (eye disease), nephropathy (kidney disease), and neuropathy will arise.
- Prevention is better than a cure. Diet is extremely important in the maintenance and prevention of diabetes and has been supported in several studies.
- “To prevent and manage diabetes, we should attain a calorie restricted, well planned low-fat and/ or low carbohydrate diet and increase physical activity. Besides changing the diet habits and lifestyle the patient should also take oral herbal preparations as these have fewer side effects.” (Pak. J. Biol. Sci., 14 (1): 13-24, 2011)
Treatment of Diabetes Type 2
Diabetes is commonly treated with medications but diabetes medications have serious side effects.
Medications and Side Effects
Metformin: A common medication used in the treatment of Diabetes. This drug lowers blood sugar by suppressing an enzyme involved in glucose production in the liver, the process of gluconeogenesis. It may cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, gas, bloating, diarrhea and a more serious side effect called lactic acidosis. The symptoms of lactic acidosis are weakness, trouble breathing, abnormal heartbeats, unusual muscle pain and light-headedness.
Glyburide: This drug lowers blood sugar by causing the pancreas to produce insulin. It will only help lower blood sugar in people who’s bodies produce insulin naturally. Some side effects include nausea, heartburn, rashes, low blood sugar, blurred vision and weight gain. More severe side effects include hepatitis, jaundice, and low blood sodium levels.
Prevention and Natural Treatments
The most important thing you can do to avoid Type 2 Diabetes is to keep an ideal body weight. This can be accomplished by eating whole foods that are high in fiber such as, vegetables, fruits, nuts, seeds and whole grains, and avoiding foods that contain bad fats (trans fatty acids), white sugar, high-fructose corn syrup, and refined carbohydrates.
Eating well and keeping your weight low and stable is very important. There are also some natural supplements that will help you to treat and prevent the complications of Type 2 Diabetes. The Hawaii Naturopathic Retreat Center works specifically with diet and lifestyle changes and will give you the tools you need to bring your blood sugar down and keep it down. What you will learn will be invaluable to your health and to the health of the people around you. I worked as an intern at the Hawaii Naturopathic Retreat Center and witnessed some remarkable transformations. Please take a look at their Type II Diabetes natural treatment and recovery program.
This article was contributed to our blog by Dr. Jennifer Heiger during her Naturopathic Doctor’s Internship at Hawaii Naturopathic Retreat Center. Dr. Jennifer Heiger was awarded her doctorate in Naturopathic Medicine from Bastyr University in Seattle, WA. She earned her undergraduate degree on the Eastern Shore of Maryland from Salisbury University. She currently resides in Seattle, WA where she shares a clinic with Dr. Gordon P. Baker, MD. who is a board certified allergist and immunologist. In addition to her medical practice, she works as a consultant for Key Compounding Pharmacy in Kent, WA. Her clinical interests include treating addiction, depression, anxiety, fatigue, digestive complaints, and hormone imbalance. Dr. Heiger believes medicine to be her art, and her passion is to build awareness that health is within everyone’s reach. She believes the body is powerful, and we all possess the innate ability to heal.
REFERENCES:
- www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- www.diabetes.org
- Glyberide (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0000833/)
- Hague, N., et al “Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus by Lifestyle, Diet and Medicinal Plants”. Pak. J. Biol. Sci., 14 (1): 13-24. 2011.