What is NAD+?
NAD+ stands for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. NAD+ is a molecule synthetized de novo from tryptophan or from the recycling of nicotinamide, salvaged from the degraded NAD+ molecule. NAD+ is found in each cell of our body under its oxidized form NAD+ or its reduced form NADH. It donates or receives an electron in redox reactions without being consumed, constantly cycling between its 2 forms: NAD+/ NADH. NAD+ was first identified as an important coenzyme in glycolysis, the energy producing metabolic cycle of the cell, therefore its other name, Coenzyme 1. Today, research has shown that NAD+ regulates many metabolic functions, in particular DNA repair and transcription. Research has shown that a decreased ratio of NAD+ to NADH is associated with chronic illness, ageing and the metabolic and behavioral changes associated with alcoholism and addiction.
NADH/NAD+ Therapeutic Uses
NADH is used orally to increase ATP, the energy currency of the cell produced in the Krebs cycle. NADH has proven to be useful in the following conditions: Parkinson disease, chronic fatigue, Alzheimer’s disease, depression and anti-aging. NAD+ is used to improve the ratio of NAD+ to NADH in drug and alcohol abuse. Increased levels of NAD+ speed up brain cell repair. NAD+ has been used intravenously in holistic addiction therapy to improve physical recovery at the molecular level, as a part of a wider approach including spiritual, mental and emotional changes.
History of NAD
Dr. Hitt Neurotransmitter Restoration Therapy (NRT)
After many years of research on the use of amino acids, minerals and vitamins to speed up the detoxification process from opiates, alcohol and other drugs, Dr. William Hitt, an American doctor and scientist, created a protocol for drug addiction recovery, known as Neurotransmitter Restoration Therapy, (NTR). This protocol addressed the neurotransmitter depletion and neurotransmitter receptor damage due to drug or alcohol overuse. Drugs produce their psychological effect by mimicking brain neurotransmitters, either by plugging into the receptor site or modifying the receptor site itself. When drug abuse ceases, the brain recovers on its own, but it may take up to a year or more. Dr. Hitt protocol speeds up this recovery time, therefore reducing the possibility of relapse due to cravings. Studies found that his protocol not only reduces cravings but limits side effects of drug withdrawal and promotes long term recovery.
Research on NRT
In the 1980’s with the support of the World Health Organization, Dr. Hitt, conducted a clinical trial in his clinic in Mexico. He administered his Neurotransmitter Restoration Therapy protocol to 3000 patients and follow them up for 3 years. After 3 years, 70 per cent of them were still sober, 2 to 7 times higher than the recovery rate of conventional approaches. After being forgotten for several years after his death, the Neurotransmitter Restoration Therapy, is coming back to life with those who worked with him and are now popularizing his treatment. NAD+ is used, not only for recovery from addiction, but also for PTSD, anxiety and depression, chronic illness and anti-aging.
“NAD has emerged as a putative metabolic regulator of transcription, longevity and several age-associated diseases, including diabetes, cancer and neurodegenerative diseases”. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, a metabolic regulator of transcription, longevity and disease Su-Ju Lin and Leonard Guarente Current Opinion www.current-opinion.com
NAD Treatment
NAD+ is administered intravenously over 10 consecutive days. The duration of the drip, up to 5 hours or more, varies according to the dosage and individual tolerance. NAD+ may be preceded by a Myers cocktail or a magnesium push to increase its tolerance and it is followed by a drip combining amino acids, vitamins and minerals, essential to neurotransmitter’s synthesis.
How Does NAD Work?
NAD+ / NADH and Brain Repair
NAD+ is absorbed by the astrocytes in the brain. Astrocytes have the important role, among many other functions, to provide nutrients to repair neurons after traumatic injury. Recent studies have shown that the administration of NAD+ can decrease ischemic brain injury. Increased levels of NAD in the neurons protects against degeneration
“Our latest studies have suggested that NADH can be transported across the plasma membranes of astrocytes, and that NAD+ administration can markedly decrease ischemic brain injury”.
NADH can be transported across the plasma membranes of astrocytes
NAD+ has a Neuroprotective Effect Against Axonopathy
“Axonopathy is a critical early event in distinct degenerative conditions including Alzheimer’s disease(AD), Parkinson’s disease and multiple sclerosis (MS),and it occurs in response to infections, alcoholism, acute chemotherapy-associated toxicity, diabetes and normal aging [33]”
NAD+ metabolism in health and disease, Peter Belenky, Katrina L. Bogan and Charles Brenner* TRENDS in Biochemical Sciences Vol.32 No.1
NAD+ and the Biology of Addiction
The compulsive need to consume a substance despite its negative health and social consequences can be viewed as the behavioral result of a neurological disorder in which the deep part of the brain is no longer controlled by the cortex. (Those deep changes in the brain have been demonstrated by MRI). All addictive substances, regardless of their behavioral effect, high, euphoria or sedation, activate the dopamine reward system of the brain and repeated use induce molecular and cellular changes in this system leading to adaptation and dependency. This biological process is the target of NAD+ administration.
NAD and Alcoholism
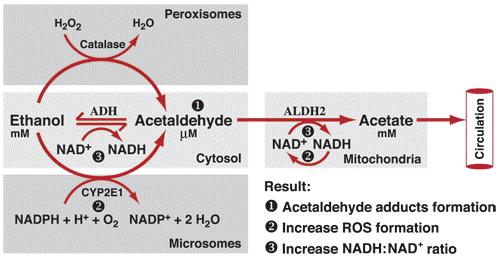
Alcohol is processed mostly in the liver. The first step in alcohol metabolism is the oxidation of ethanol to acetaldehyde and NADH catalyzed by the enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase containing NAD+. Acetaldehyde is a toxic compound that eventually harm the mitochondria and the liver.
CH3CH2OH + NAD+ —> CH3CH=O + NADH + H+
Large consumption of alcohol produces an excess of Acetaldehyde and NADH that cannot be processed by the liver to the final form of acetic acid. Some acetaldehyde and NADH escape in circulation and reaches the brain where it alters neurotransmitters and causes the known behavioral effects of alcohol intoxication. The excess of acetaldehyde and NADH in the liver is the cause of the metabolic effects of alcohol: hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia depending on whether glycogen stores are adequate, inhibition of protein synthesis, elevations of triglycerides which accumulate in the liver resulting in fatty liver and hyperlipidemia. The elevated ratio of NADH to NAD and elevated acetyldehyde is also the cause of the addictive effect of alcohol as demonstrated by recent studies.
“Recent investigations have suggested that acetaldehyde may be responsible for the development of alcohol addiction. Acetaldehyde in the brain may inhibit enzymes designed to convert certain nerve transmitters from aldehydes to acids. The nerve transmitters that accumulate may then react with the acetaldehyde to form compounds which are startlingly similar to certain morphine-type compounds”.
A number of metabolic and psychological effects from alcohol are directly linked to the production of an excess of both NADH and acetaldehyde.
NAD+ and Cravings
Cravings combined with the lack of control of the cortex over impulsivity lead to relapse. The biology of cravings is deeply seated in the brain neuronal circuits changes in response to chronic drug use. Studies have shown that NAD+ can help repair these circuits and reduce drug cravings
The following study was conducted about the effect of NAD+ on addiction –
500 mg to 1500mg of NAD+ was administered to 60 patients for 10 days daily over a period of time of 5 to 10 hours. Cravings were rated at the beginning of the treatment, at 5, 10 days and 12-20 months.
The study reports a decrease in cravings for stimulants opiates and alcohol 5 days after the starting of the treatment
of excess NADH generated by ethanol oxidation
